3 Classifications of E-bikes You Have to Know
Electric bike laws in the United States differ by state, as each state has the authority to set its own regulations regarding e-bikes. However, the federal government has established some general guidelines that apply to e-bikes. Here are some key points to consider:
Types of Bike
E-bikes are usually classified into three categories based on their maximum assisted speed and method of operation.

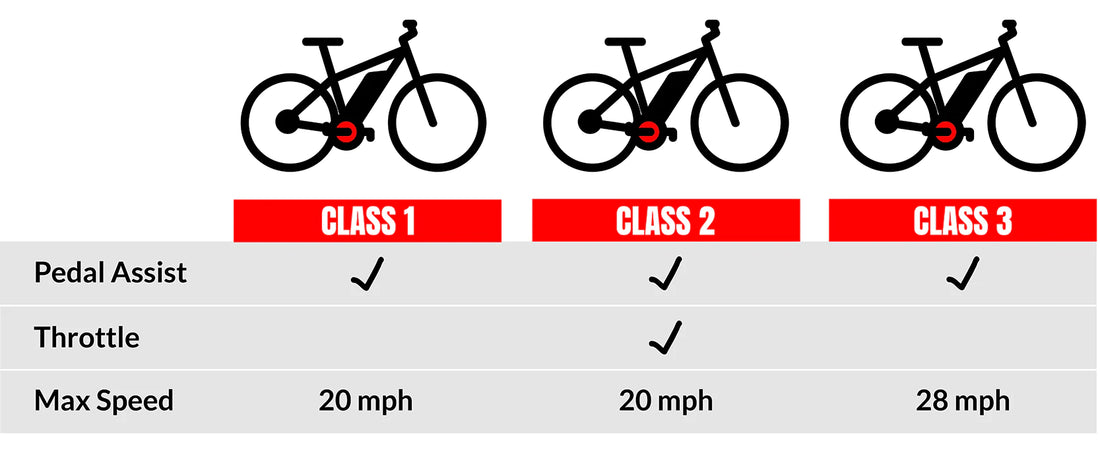
Class 1 E-bikes
Bicycle with a motor that only provides assistance when the cyclist is pedaling and doesn't provide assistance over 25 mph.
Class 2 E-bikes
Bicycle with a throttle-actuate motor that doesn't provide assistance over 20 mph.
Class 3 E-bikes
Bicycle with a motor that only provides assistance when the cyclist is pedaling and doesn't provide assistance over 28 mph.
The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) has established federal regulations for e-bikes, particularly those with pedal-assist capabilities. These regulations define the three classes mentioned above.
- State regulations may also apply. States can regulate the use of e-bikes within their borders, including specifying where they can be ridden and whether helmets are required.
- Local regulations may also apply, so it's important to be aware of them to ensure compliance.
- Some states require helmets for e-bike riders, while others do not. It is important to review the regulations in your state regarding e-bikes.
- Age restrictions may apply to certain classes of e-bikes. For instance, some states may require riders to be of a certain age to operate a Class 3 e-bike.
Additionally, regulations may dictate where e-bikes are permitted to operate. While some states allow e-bikes on bike paths and trails, others may restrict their use in certain areas.
Due to the variability in regulations, it is crucial to check the specific laws in your state regarding electric bikes.